Digital content creation is booming, with an astonishing 2.5 quintillion bytes of data produced daily.
While everyone has the ability to create content at their fingertips, making your digital voice stand out is increasingly challenging.
Onboarding a system that allows you to create, integrate, and manage your content could be the missing piece in your digital toolkit.
This article outlines the key features and benefits of content management systems to provide you with the insights you need.
What is a CMS?
A content management system (CMS) is a software application that allows users to create, edit, manage, and publish digital content—typically for websites—without needing specialized technical knowledge like coding.
How Does a CMS Work?
Without a CMS, If you want to create content, you will need to write an HTML file and upload it to your server.
A CMS works by allowing you to create, edit, and manage a website without needing to know how to code.
Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Create Content: You write and add images or videos through an easy-to-use editor, like typing in a word document.
Store Content: The CMS saves your content in a database, so it can be used later.
Design with Templates: The CMS uses a template to make sure your content looks good and fits with the overall design of the website.
Publish: When you're ready, you hit "publish," and the CMS makes your content live on the website.
Manage Easily: You can manage the content from a user-friendly dashboard, without worrying about the technical side.
By using a CMS, the content you create will show up for your audience exactly how you want it to look.
Structure of a CMS
A CMS typically consists of two main components:
- Content Management Application (CMA)
- Content Delivery Application (CDA)
Understanding these components is essential for effectively using a CMS. Here's a simple guide to each part and how they work together.
1. Content Management Application (CMA)
The CMA is the user-facing side of the CMS. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that allows users to:
Create Content: Easily add new pages, blog posts, images, videos, and other media without writing code.
Design Layouts: Use templates and themes to change the look and feel of your website.
Edit and Update: Modify existing content, correct errors, or update information as needed.
Organize Content: Categorize and tag content for better navigation and searchability.
Manage Users: Assign roles and permissions to team members, such as authors, editors, and administrators.
Optimize for SEO: Utilize built-in tools to improve search engine rankings through meta tags, keywords, and URLs.
Key features of CMA
WYSIWYG Editor: "What You See Is What You Get" editors allow you to format text, insert images, and embed videos without HTML knowledge.
Drag-and-Drop Functionality: Easily rearrange page elements to customize layouts.
Version Control: Keep track of content changes and revert to previous versions if necessary.
Multilingual Support: Create content in multiple languages to reach a wider audience.
2. Content Delivery Application (CDA)
The CDA is the backend process that handles content delivery to your website visitors. It takes the content entered through the CMA and:
Stores Content: Saves content in a database in an organized manner.
Processes Requests: Fetches and compiles content when a user accesses your website.
Delivers Content: Renders the content into HTML and other web formats for display on various devices.
Manages Security: Implements security protocols to protect against threats like SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
Ensures Performance: Optimizes load times through caching and content delivery networks (CDNs).
Key features of CDA
Scalability: Handles increased traffic without compromising performance.
Reliability: Ensures uptime and quick recovery in case of failures.
Integration: Works seamlessly with third-party services like payment gateways, analytics, and marketing platforms.
Compliance: Adheres to data protection regulations like GDPR.
Types of CMS
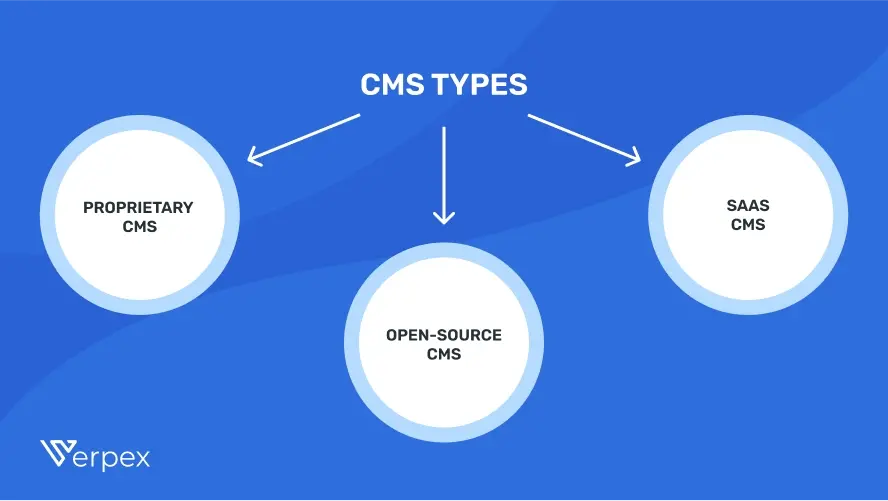
CMS types vary based on how they are integrated into your system:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Proprietary CMS | Built by a single organization, it requires purchasing a license and paying for upgrades, customization, and ongoing support. |
| Open-Source CMS | No initial cost or licenses needed, but you’ll need to handle updates, plugins, customization, and technical support during setup. |
| SaaS CMS | Includes support, web content management, and hosting in one package. You pay based on a subscription plan, which covers support, data transfer, and content storage. |
Basic functions of CMS
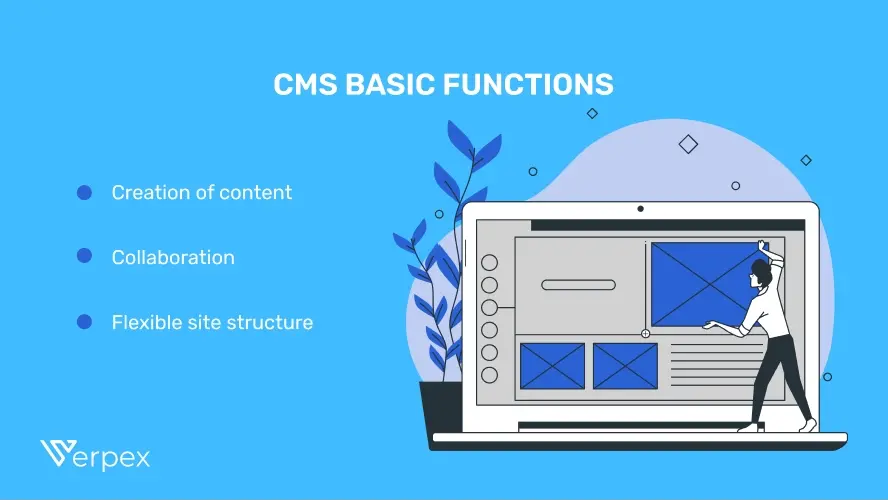
Creation of content: A CMS allows you to make certain aspects of content creation easier, by utilizing industry-specific tools that are built in the software.
These can be whole applications that have a detailed aim, or simple widgets you can use.
Collaboration: With a CMS, you are able to collaborate with a whole team of people so you can work simultaneously on certain content.
You can’t foul up other people’s contributions because the CMS keeps track of every change made.
Flexible site structure: Each user is able to customize the structure of the website content. You can also segregate the content based on tags, categories, and so on.
You can make easy changes in the content templates and the overall appearance with basic skills.
Version Control: CMS platforms often provide version control, allowing users to access and revert to previous versions of content if needed, making it easy to manage changes over time.
User Permissions: CMSs allow admins to assign different permission levels, ensuring that only authorized users can make specific changes to content or settings.
SEO Optimization: Most CMS platforms include built-in SEO tools to help optimize content for search engines.
These tools assist with keyword management, metadata, and other features to improve website visibility.
CMS Features
Social media integration
Optimize your content for social media platforms and add social media sharing buttons to your pieces of content.
Thorough Analytics
Your CMS should integrate analytics tools as tracking engagement is an essential part of the content strategy.
Security
You need to make sure that your website protects the data of your customers, as well as your company’s data.
Why Do You Need a CMS?

A CMS brings many advantages to small companies, startups, and enterprises.
Here are a couple of reasons why:
Easy to use
For non-developers, a CMS makes it easy to fill out a form and automatically create a page. Without a CMS, even small changes, like updating a title, would require a developer.
Even for developers, a CMS saves time by avoiding the need to rewrite code for every update.
Cheaper than hiring a developer
Hiring a developer to build a user management system and content management features will be costly.
For frequent updates, a CMS is a more cost-effective solution.
Scalability and flexibility
As your business grows, a CMS allows your website to grow with it.
You can easily add new pages, features, or functionalities (like e-commerce or a blog) without needing to rebuild the site from scratch.
This flexibility ensures that your website evolves with your business needs.
No coding knowledge required
As we previously mentioned, you don’t need any coding experience to use CMS.
This software provides people who don’t have any coding background with the chance to create a site that is completely functional.
Your web content can be easily uploaded to your website.
Easy collaboration
A CMS allows different people to collaborate on projects. Multiple people at a time can add, update, or edit content from their own computers.
Developers can customize the theme, IT can handle security, and marketers can create content, all at the same time.
SEO features and extensions
A CMS provides numerous tools and plugins that will help your site rank better in search engines.
Using third party tools, you can optimize page load times, create 301 redirects, add image alt text, create XML sitemaps and choose URL structures that are SEO-friendly.
Predesigned templates
Many CMS platforms offer a range of predesigned templates that you can use to customize your site.
A good template helps with content creation by guiding you to add categories, tags, and resize images, saving you time on small details.
Simple updates
With a CMS, you can make changes on your site, no matter how small or big, in no time. You can do all of these changes yourself, instead of hiring a developer to do it for you.
Support
Even though not all software offers support, the more popular ones like Drupal or WordPress have an engaged community which runs forums and wikis.
If you’re not a company that has IT specialists, these features can be quite useful when you run into a problem.
What Kinds of Websites Can You Build with a CMS?
Even though there is a general misconception that a CMS is just for blogging, the truth is that CMS is so flexible that it can be used for almost any type of website you want.
However, CMSs are ideal for websites that are based around creating and sharing content.
This means that they are ideal for:
- Tutorial websites
- News and Media
- Portfolios
- Simple blogs
- eCommerce stores
- Online communities
- Multi-site networks
- Multilingual sites
Using the right tools, you can even create forums, private membership sites, and online stores.
8 Steps to Build a Website with a CMS
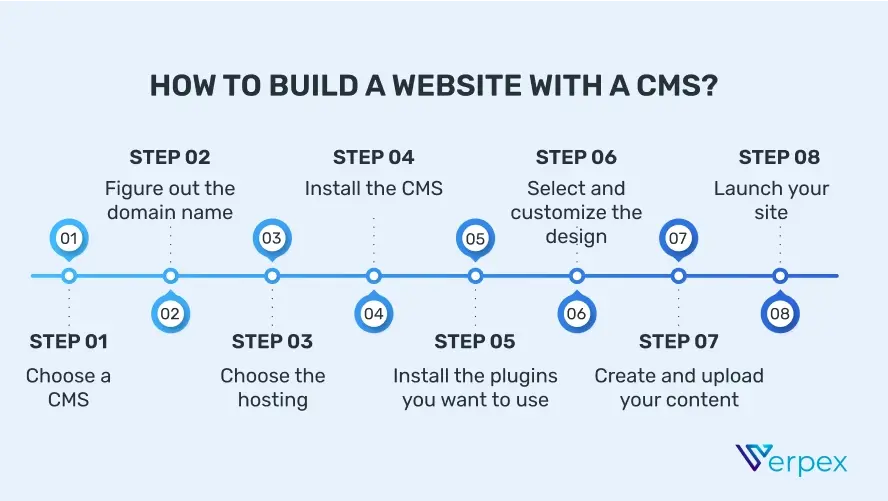
In order to create a website with a CMS, you need to follow these steps:
1. Choose a CMS: There are several options out there, so choose the right one for you
2. Figure out the domain name: Choose a simple, yet memorable domain name for your site
3. Choose the hosting: Since not all CMSs come with integrated hosting solutions, select your hosting plan
4. Install the CMS: Once you’ve chosen your CMS, it’s time to install it
5. Install the plugins you want to use: Choose the plugins you want to use for your site and install them
6. Select and customize the design: Select a suitable theme for your site and work on customizing the design
7. Create and upload your content: After you’re done with the design, it’s time to upload some content
8. Launch your site: The final step is to go online.
Examples of CMS
WordPress
WordPress is a popular CMS known for its wide range of templates, design customization tools, large user community, and extensive integration options.


Joomla
Joomla is another popular platform, but it's less beginner-friendly and requires more skills and effort. It's open-source and can be used for various websites, like landing pages and business projects.
Drupal
Drupal works well for businesses of any size. It offers extensive design customization and user management options, making content uploading quick and secure.


Magento
To fully use Magento's features and extensions, it requires some effort to learn. However, once mastered, it's highly secure and flexible, allowing you to manage multiple stores, transact globally, and use various shipping providers.
Shopify
Shopify is an easy-to-use CMS built for e-commerce. It has tools for managing online stores, like product listings, payment options, and shipping features, making it great for businesses of all sizes.


Wix
Wix is an easy-to-use, drag-and-drop website builder that also functions as a CMS. It's perfect for beginners and small businesses to create professional websites without technical skills.
Squarespace
Squarespace offers stylish templates and an easy-to-use interface, making it popular for creatives, portfolios, and small businesses. It supports blogging, e-commerce, and design customization.

How to Choose the Right CMS for Your Business
Selecting the right Content Management System (CMS) is crucial for your business's online success.
Here's how to make an informed choice:
Assess your technical skills
- User-friendly interface: If you're not tech-savvy, opt for a CMS that's easy to use without coding knowledge.
- Developer flexibility: For businesses with in-house developers, a CMS with advanced customization options may be suitable.
Define your business needs
- Website purpose: Determine if you need a blog, ecommerce site, portfolio, or a combination.
- Scalability: Choose a CMS that can grow with your business and handle increased traffic.
Consider your budget
- Initial costs: Look at licensing fees or subscription costs if applicable.
- Ongoing expenses: Factor in costs for hosting, plugins, themes, and maintenance.
Check customization options
- Templates and themes: A wide selection allows for better brand alignment.
- Plugins and extensions: Ensure the CMS supports the functionalities you require.
Evaluate integration capabilities
- Third-party tools: The CMS should integrate seamlessly with your existing software like CRM, email marketing tools, and analytics.
- API availability: For custom integrations, check if the CMS offers a robust API.
Prioritize security features
- Regular updates: A CMS with frequent updates is more secure against threats.
- User permissions: Ability to set different access levels for team members enhances security.
Look for SEO-friendly features
- Built-In SEO tools: Features like meta tag editing, SEO-friendly URLs, and sitemap generation are essential.
- Performance optimization: Fast loading times contribute to better search rankings.
Test for mobile responsiveness
- Responsive design templates: Ensure the CMS offers mobile-friendly themes. Mobile editing tools: Ability to manage your site from mobile devices adds convenience.
Analyze content management features
- Version control: Helps track changes and revert to previous versions if needed.
- Multilingual support: Important if you have a global audience.
Final Remarks
Content Management Systems offer many benefits, including SEO features, flexibility, cost-efficiency, easy maintenance, quick setup, and user-friendliness.
To maximize these advantages, define your technical needs, workflows, and processes.
Choosing a CMS can be challenging due to the variety of options.
Consider the tools, integrations, features, and hosting options to ensure you choose a system that best supports your goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need a MAC or a special PC to use a CMS?
No, you don’t. Any computer with a web connection and an installed browser should be just fine.
Is a CMS hard to use?
No. CMSs can be used with minimal training, and you don’t need a programming background in order to use one.
Is there more than one Content Management System?
Absolutely! There are hundreds of CMSs available, and they all work in different ways.
What is the best CMS?
Everyone has their own favorite CMS, but the best one for you is the one that matches your business requirements.
What are the three components of CMS?
No, a CMS (Content Management System) is not a CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system.
A CMS manages website content, while a CRM manages customer interactions and relationships.

I've been navigating the web hosting waters for years now. As the Chief Editor at Verpex, I team up with some awesome writers to dish out the good stuff on hosting. Got a Master's in Journalism, so I always have an eye out for quality. Whether you're just dipping your toes or you're a seasoned surfer, I'm here to make everything web hosting feel like a breeze
View all posts by Julia Lozanov