When the term "duplicate website" or "cloning website" is mentioned, the first thought that pops up in our mind is "illegal,” which is correct; cloning a website based on malicious intent is considered illegal and a violation of intellectual property under copyright law.
However, just as criminal hacking exists, so does ethical hacking, e.g. "White Hat".
Duplicating a website can serve many legitimate purposes—testing, redesign, development, or backup.
This guide walks you through the most effective ways to duplicate a website, along with important legal notes and post-clone checks.
What Does It Mean to Duplicate a Website?
A duplicate website is a full or partial copy of an existing site—this includes its layout, visual design, code, and sometimes its content.
To duplicate a website means to create an exact or partial copy of its structure, codebase, and content. Depending on your goal, this could involve front-end HTML and CSS, server-side code, databases, or all of the above.
To make a duplicate website is to recreate how a site functions and appears, often using the original structure as a foundation. This process might involve copying front-end elements (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), backend functionality, databases, or even configuration files. Whether you're aiming to copy a website for testing, reuse, or research, the key is to work within ethical and legal boundaries.
Why Duplicate or Clone a Website?
There are many valid reasons to duplicate a website or clone a website, especially in professional and development-focused environments. These methods are often used by developers, designers, and site owners who need to make a duplicate website for functional or strategic purposes.
Common use cases include:
To Serve as a Backup: Duplicating is another means of backing up a website, for instance, in the case of mayhem, the website can be restored to itself with all of its data.
For Geo-Targeting: Versions of a website are made to target certain geographical regions. e.g. certain regions may have laws that must be complied with, to do so, you may have to customize a website that complies with the regulations and requirements. In this case, duplicate websites are made to save the process of building a website from scratch.
Recycle/Customization Purpose: Sometimes, websites are copied to build upon their structure and add new elements to make them stand out, much like a template or blueprint for creating another website with the same features. It is quicker to do this than to start from scratch.
For Analysis: A Website can be cloned to examine the elements or structure. You may want to study a website through and through to understand its strengths and weaknesses, design, elements, and structure. However, this should be done only for research purposes and legally to avoid legal issues.
For Testing and Development: Developers may clone a website for the purpose of testing and development. For instance, if they need to add features or functionalities to a live website, the cloned website would be tested first to see how well these features or functionalities work before they are integrated into the live website, this is to avoid crashing the website.
Additional scenarios include:
- Migrating a site to a new domain or hosting provider while maintaining structure
- Creating a staging environment to present updates before going live
- Studying website performance through load testing or optimization comparisons
- Developing client variations using a copy of an existing layout
- Reusing internal templates for faster deployment across similar projects
- Training or documentation where a working website is needed for walkthroughs or tutorials
- Ethical hacking and security reviews in a controlled environment, following white hat principles
- Learning how websites work by duplicating a personal or test site for hands-on experimentation
These use cases help streamline workflows, improve reliability, and reduce the risks associated with direct changes to a live site.
Before You Duplicate a Website
1. Intent: The intent behind building a duplicate website must be taken into account; it might be for testing, educational purposes, etc. As a result, you will know what approach to use when duplicating a website.
2. Technical Knowledge: In order to duplicate a website, you must possess technical knowledge. This will enable you to choose the appropriate techniques or tools for the site's structure, dynamic content, functionalities, and other technical aspects involving databases, server-side languages, hosting, etc.
3. Copyright Laws: If it’s an open-source project, you can clone the repository and make changes to it. In the event that it isn't, it's crucial that you understand the legal and copyright repercussions of copying a website. Copyright laws protect websites, so unauthorized duplication may have legal repercussions unless you work for an organization that permits it, in which case it would be a work project or duplicating your own website. You must make sure that you’re not violating any laws to avoid legal issues.
4. Hosting Environment: Your hosting platform should support the same technologies used by the site you're duplicating. If you're planning to clone a website for development or testing, match the original environment as closely as possible.
5. SEO and Indexing Risks: If the duplicate will be online, block it from being indexed using robots.txt or noindex tags. Accidentally indexing a copied website can lead to SEO penalties and duplicate content issues.
6. Data Sensitivity: Avoid duplicating sensitive user data. If you're working with real content, be sure to remove or anonymize personal information—especially when following white hat or ethical hacking practices.
7. Tool Selection: The tools you use to copy a website should fit the site type. Static sites can be duplicated with software like HTTrack, while CMS-based sites often require plugins, database handling, or version control systems.
8. License Compliance: Even if a website uses open-source code, always check the license. Some licenses allow modification and reuse, while others require attribution or restrict commercial use.
4 Ways to Duplicate a Website
There’s more than one way to copy a website, and the method you choose depends on what kind of site you’re duplicating— static vs dynamic, your technical skill level, and your goals. Below are four common ways to make a duplicate website, whether you're building a backup, setting up a staging environment, or creating a learning sandbox.
1. Website Copying Tools (e.g. HTTrack)
Best for static sites that don't rely on server-side logic or databases.
2. Browser Extensions (e.g. Save All Resources)
Useful for downloading front-end assets and layouts from simpler websites.
3. Version Control with Git
If the website is stored in a Git-based repository, developers can duplicate it using either of the following:
- Git Clone: Run
git cloneto copy a repository to your local machine. This gives full access to the source code for editing and testing. - GitHub Fork: Fork a repository on GitHub to create a personal version. You can then clone it locally and propose changes via pull requests if needed.
This method is ideal for open-source development, collaborative work, and white hat testing environments.
4. Manual File + Database Duplication
For CMS-based or dynamic sites (e.g. WordPress, Joomla, Laravel), this method gives you full control.
Quick Comparison: Ways to Duplicate a Website
| Method | Best For | Captures Backend? | Requires Technical Skills |
|---|---|---|---|
| Website Copying Tools | Static websites and offline browsing | ❌ | Low to Medium |
| Browser Extensions | Front-end layout review or design reference | ❌ | Low |
| Version Control with Git | Developer projects stored in code repositories | ✅ (code only) | Medium to High |
| Manual File + Database Duplication | Full CMS sites, migrations, or staging setups | ✅ (full site) | High |
1. Copying Tools
Duplicating a website is more difficult than it appears because there are numerous functionalities required. There are technologies available that can effortlessly copy websites, speeding up the process of developing a website from the start.
After copying the source code to your local computer, you can host it on your server. However, if the website does not belong to you, duplicating it without permission is considered bad practice. Website copying software examples include HTTrack, ArchiveBox, Cyotek Webcopy, and others.
The first step in using any of the copying software mentioned above is to download and install the program; in this case, we'll be using HTTrack.
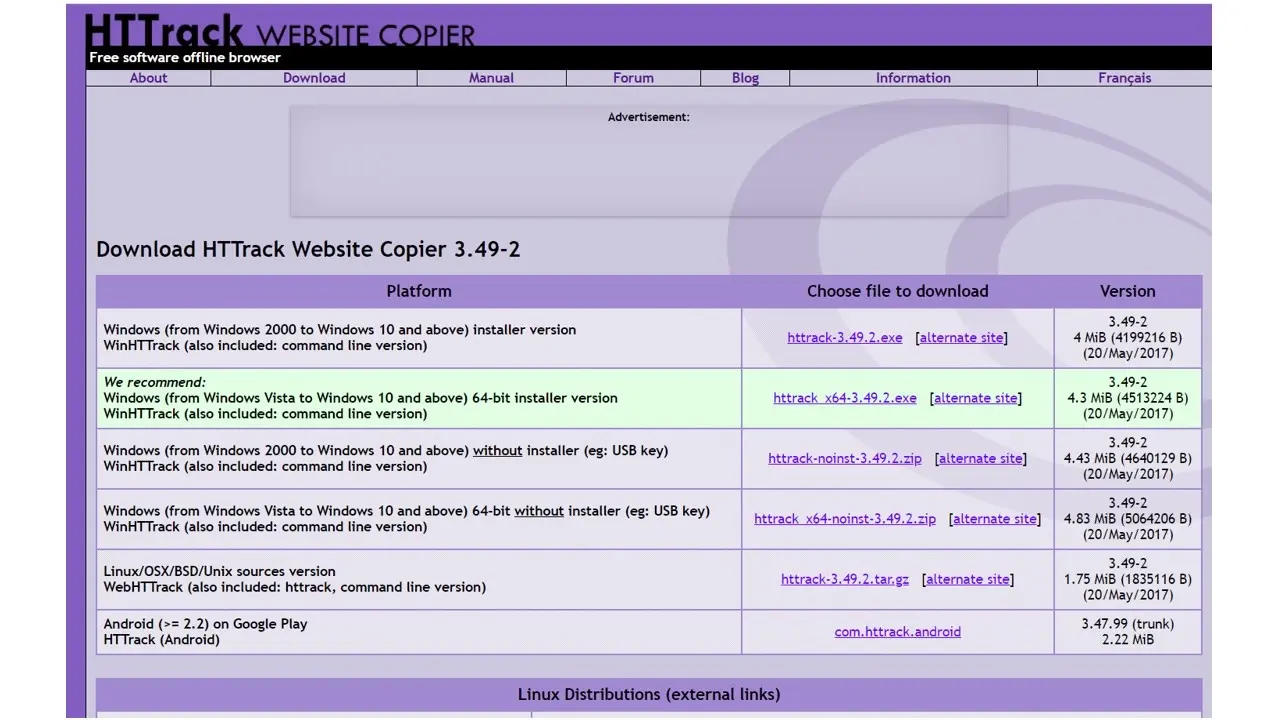
After installation, all you need to do is type the name and project category (you can skip this step) and select the path where you want the project stored.
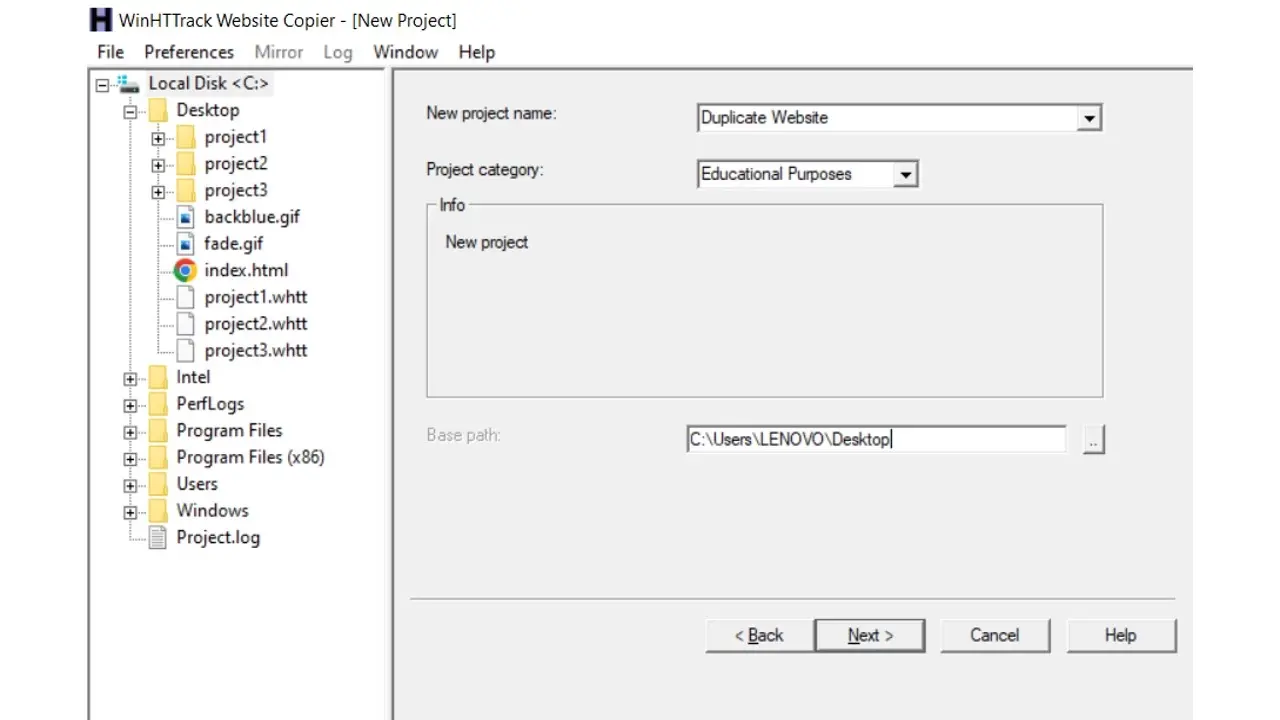
The next step requires that you enter the URL of the website you want to copy;
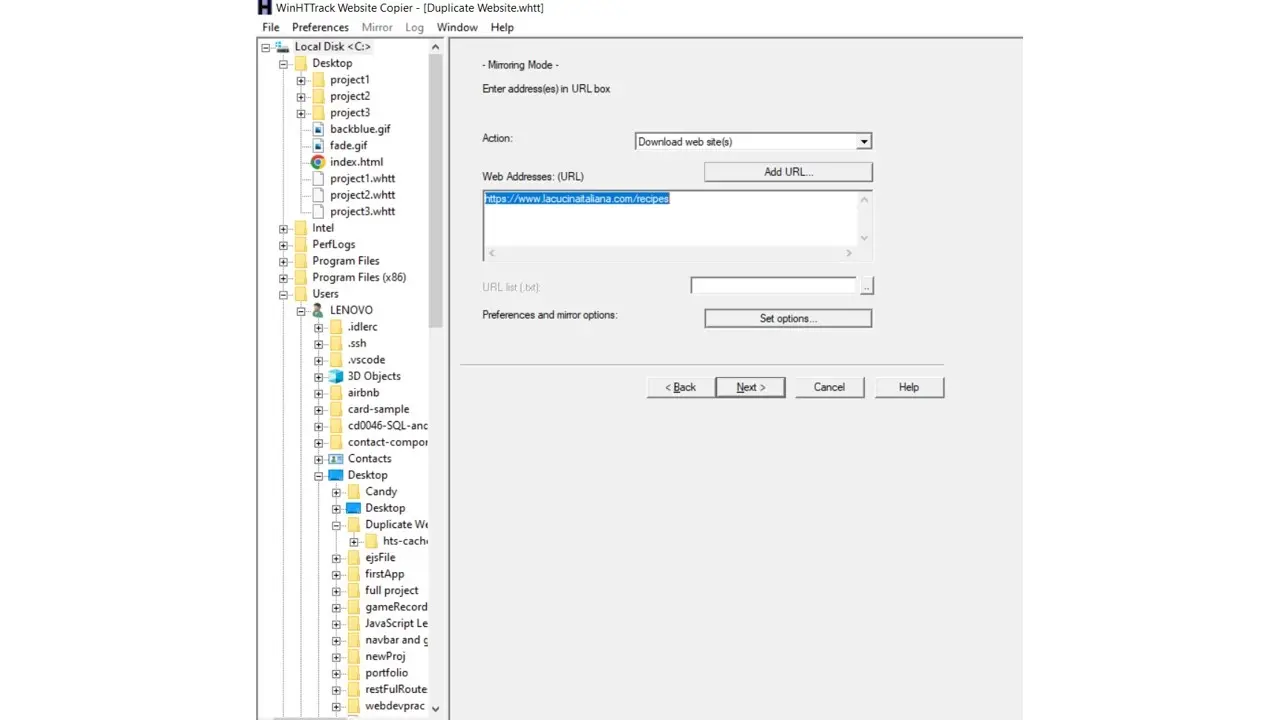
Start the duplicating process;
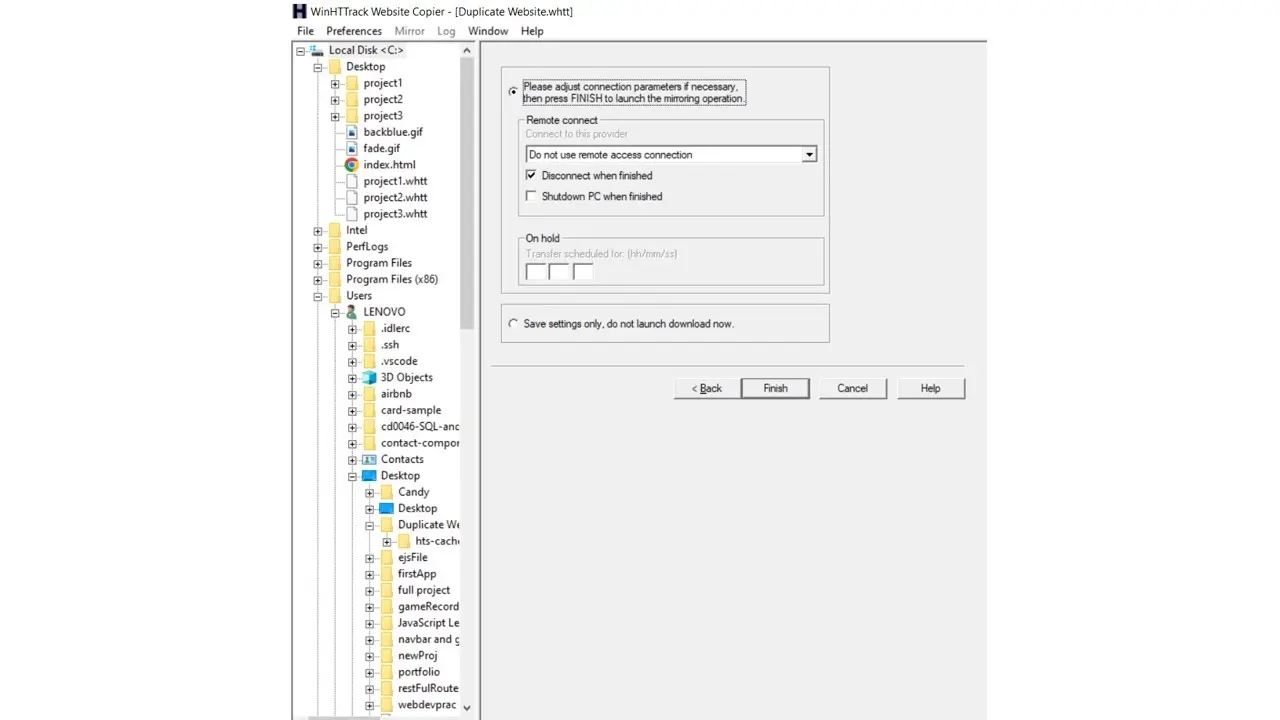
After you click Finish, HTTrack will begin to crawl and copy the website, which will then be hosted on your local machine. This process may take a while, depending on the size of the file.
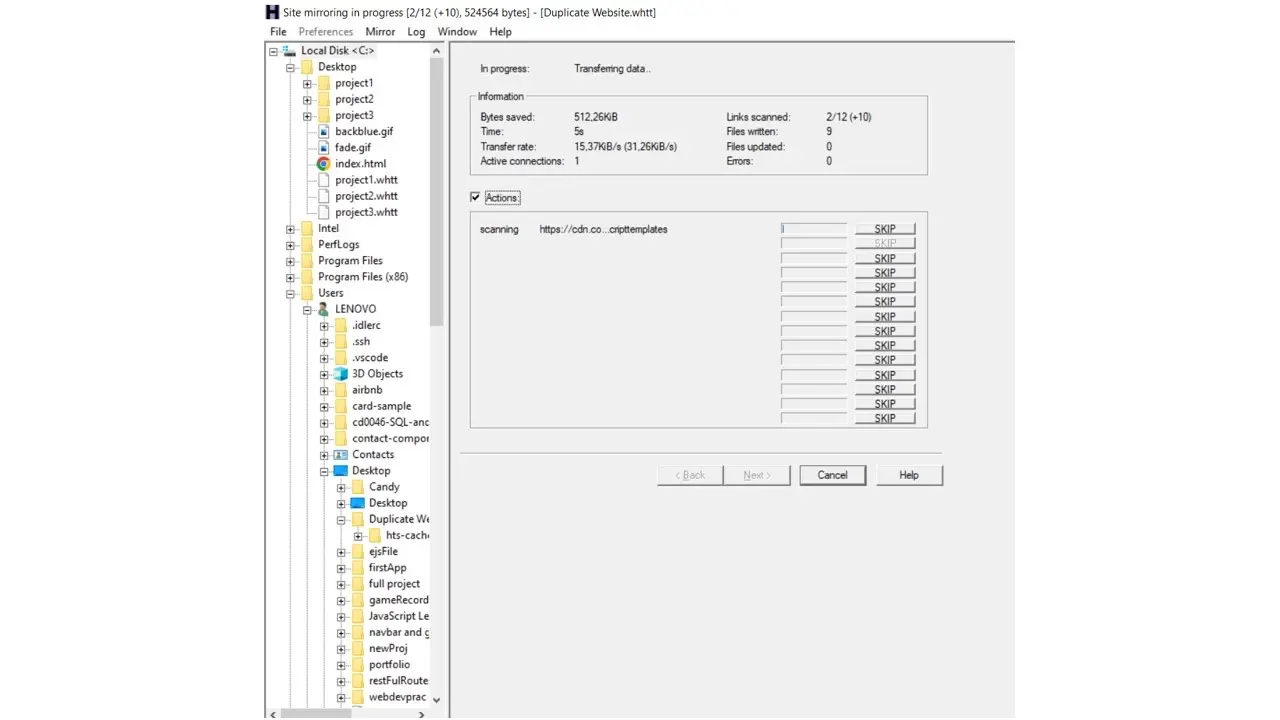
After it’s done copying, you can browse the mirrored website. If we take a look at the image below, we’ll see the duplicated website beside the main website. Notice that the URL is different; the duplicated website is hosted on our local machine (HTML file)
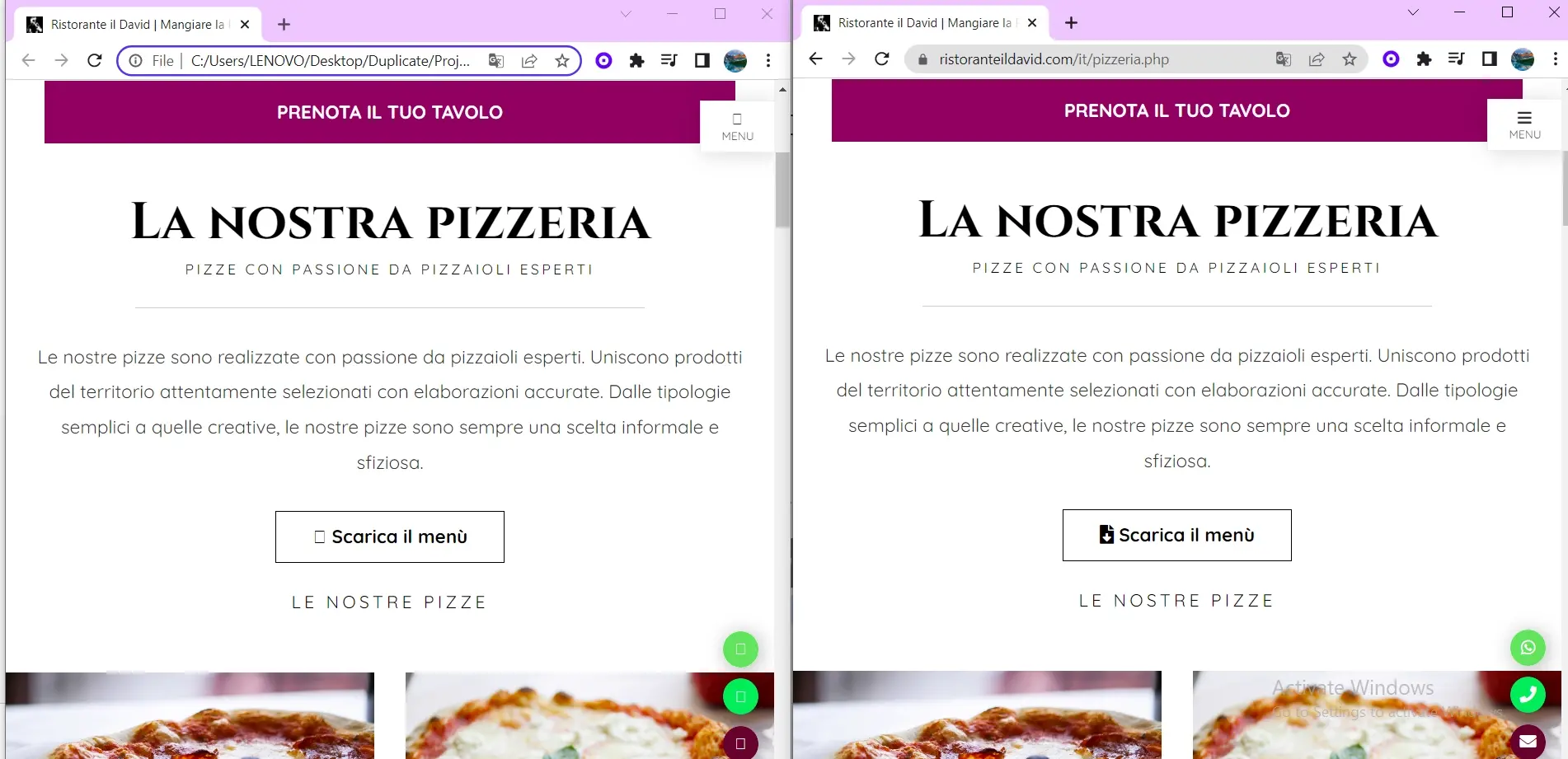
2. Copy Source Code via Extension in Chrome
To download the source code of a website, we can use an extension in the Chrome Web Store named Save all resources. We'll add this extension to begin.
Open the website you want to duplicate, right-click, and select the inspect option; it’ll show the dev tools. Click on "more options" >>, and you’ll find Resource Saver.
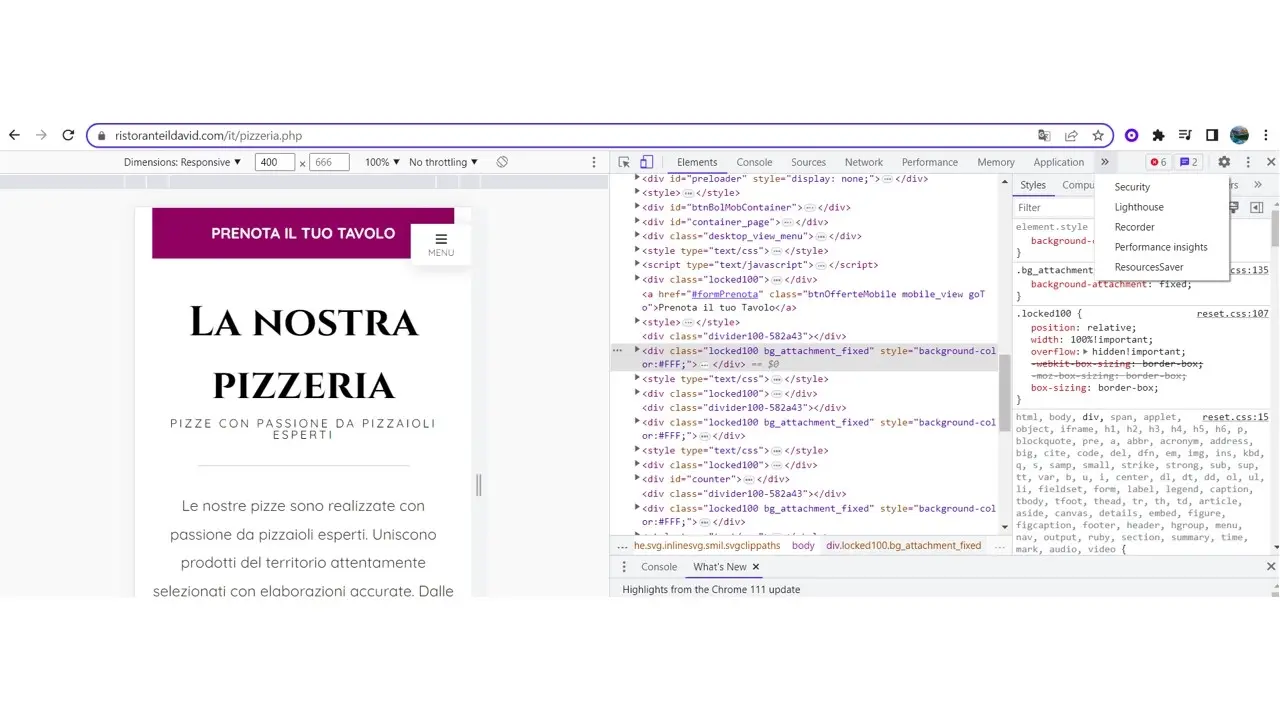
Select Resource Saver, tick the boxes, and select Save All Resources.
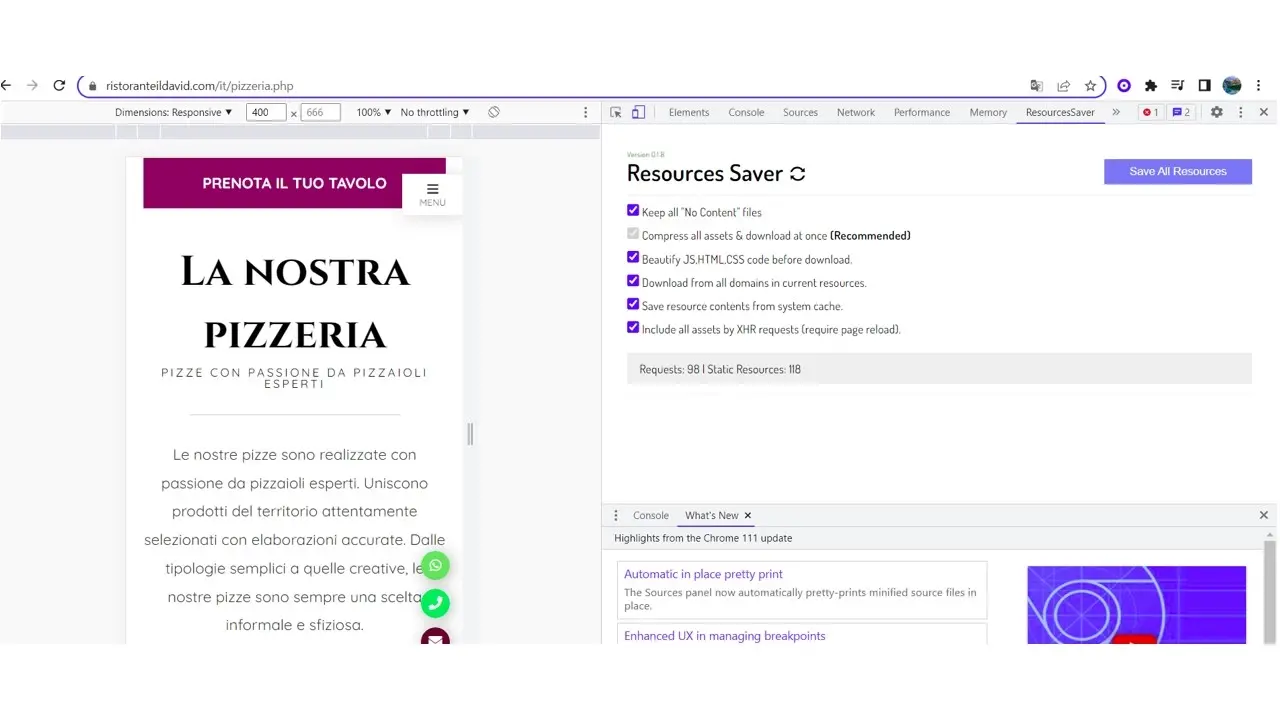
This will download all the resources to your computer, check your download, and extract the file to open the folder. Enter the folder, search for the HTML file, and open it in your browser to confirm that it works.
3. Version Control Software
Development teams or individuals can manage projects using version control software; the most popular example is Git.
Git is a version control system distributed under the General Public License (GPL), which allows users to use, share, and modify it for free; this is termed "open source".
Using Git, developers have access to all the source code, and development teams can work on small or large projects in a distributed server environment. To use git to duplicate a website, the website file should already be saved to GitHub.
Note: GitHub is a hosting service for git-based program management and version control. This article will help you learn more about Git, Github, and the commands involved in creating and pushing a repository to GitHub.
4. Git Clone or GitHub Fork Feature to Duplicate a Website
There’s a difference between both commands, and we’ll go over them for clarity.
Git Clone:
The command [git-clone] is used to duplicate or clone a repository into a new directory. It is used to make a duplicate of an existing repository. You can make modifications to a repository after cloning it without impacting the original version. All you have to do to implement these modifications is push the changes back to the repository.
Create a new folder where you want the files to be saved, and copy the path, or you can create a folder in Git Bash by using mkdir.
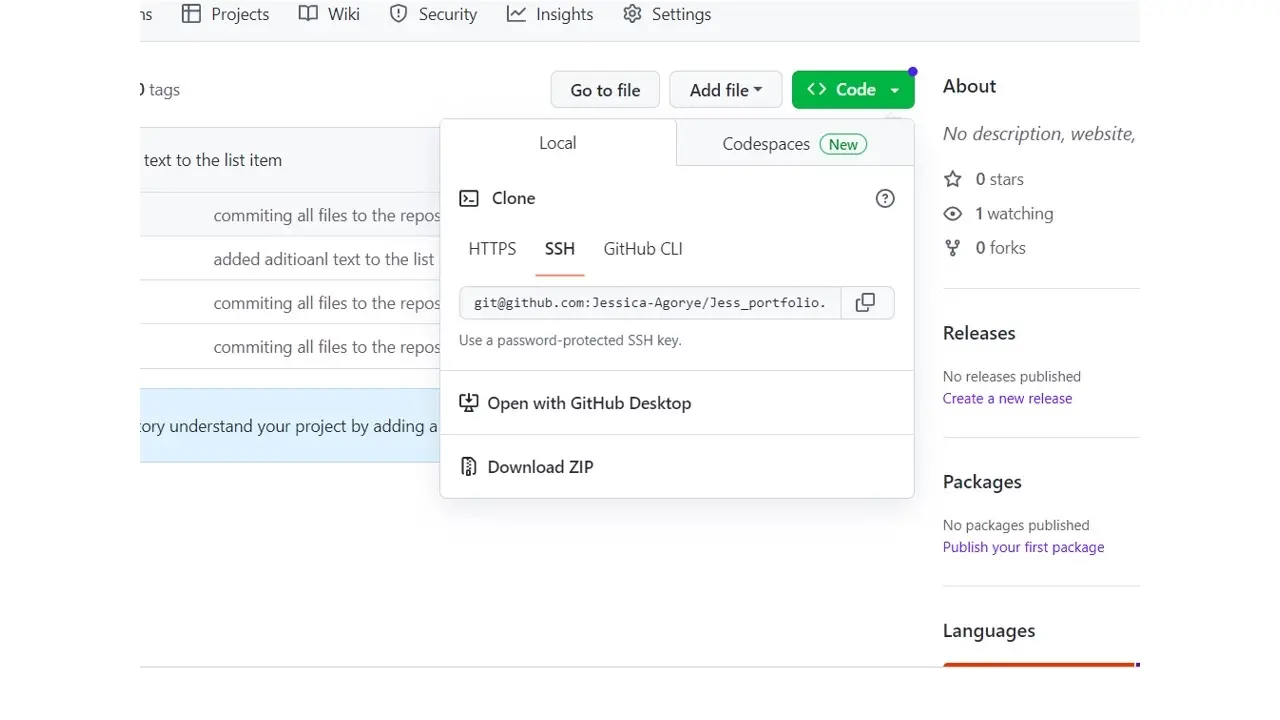
Open Git Bash, enter into the folder by using the cd command, and paste the path e.g cd “ C:\Users\LENOVO\Documents\clone folder”
Go back to GitHub and copy the SSH URL, in the git bash, type git clone “insert copied URL” e.g git clone “[email protected]:Jessica-Agorye/Jess_portfolio.git”
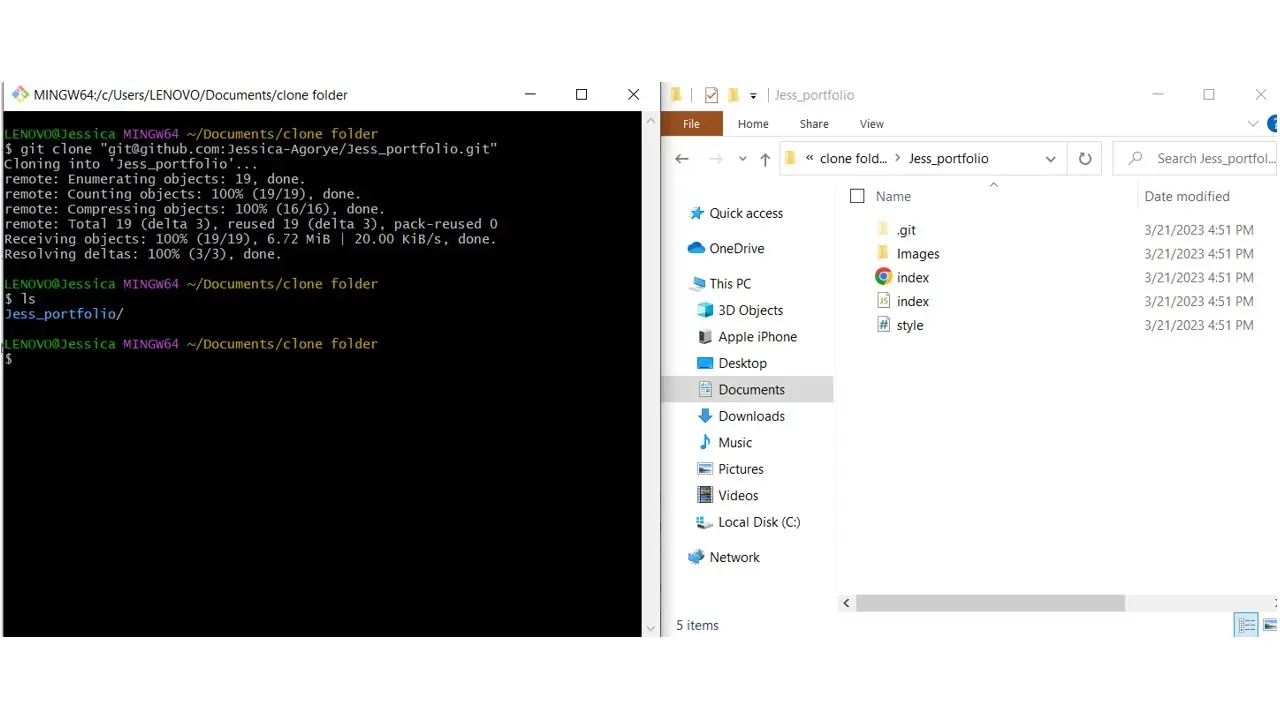
If you use the VSCode IDE, you can simply open it directly from git bash by typing “code .”, as seen in the image below.
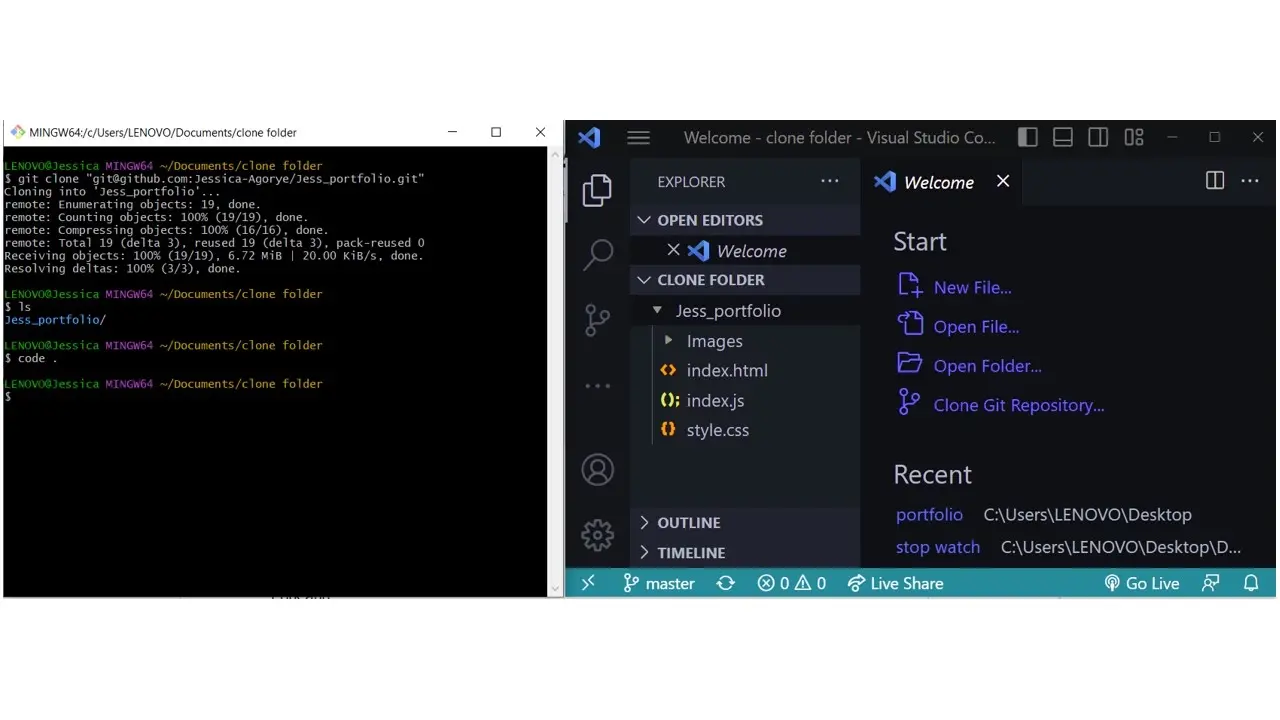
We can see from the example that we’ve successfully cloned our GitHub repository.
GitHub Fork Feature:
The fork feature on GitHub is used to duplicate a website; this is used to isolate a file to have full control over it. To fork a repository, all you have to do is click on “fork"
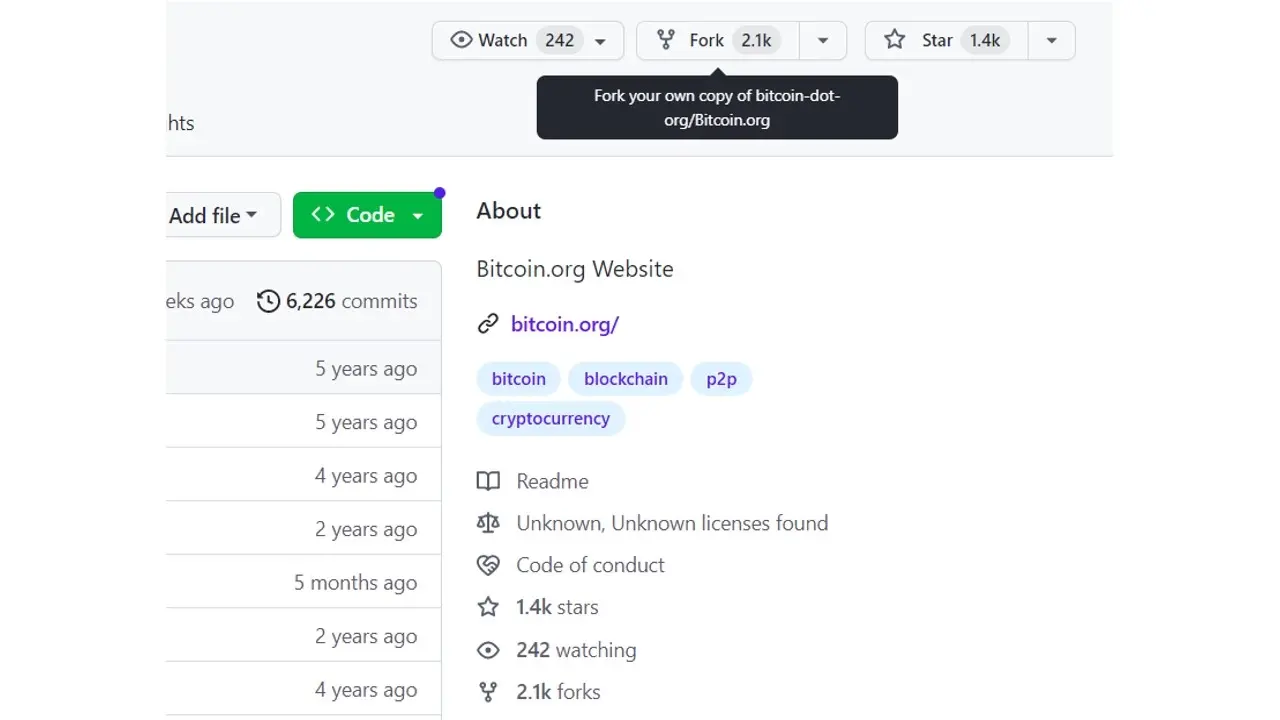
This will make an individual copy of the repository, which you can then clone with git clone to have access to the files in your local workspace.
Note: The distinction between GitHub's "git clone" and "fork" features is the level of control developers have over the repository.
When you clone a website or a repository, you can work on it locally; however, you cannot submit changes to the file unless you are part of the project team. You can only push modifications to the forked file using a pull request; however, the owner must determine whether or not to pull your changes.
Risks of Duplicating a Website Illegally
The majority of websites are secure against crawling software. The Robots.txt file, for example, is used to tell search engines and other automated tools not to crawl a website.
Copying tools are used by hackers to clone websites and fool people into providing essential information for the goal of theft or other harmful intent. It is also considered copyright and trademark infringement, both of which are illegal. Duplicating websites might harm your reputation, which will harm your brand. It's fantastic to be inspired by a brand for the sake of learning. It is less likely to cause problems if permission is obtained to clone a website for work purposes.
Additional risks include:
- Copyright infringement: Even copying a small part of a site—like text, images, or design—can violate intellectual property laws.
- Trademark violations: Duplicating branding elements like logos or domain structure can trigger legal action.
- Search engine penalties: If search engines detect duplicate content, your site may be flagged or deindexed.
- Security blacklisting: Hosting a cloned site without consent may lead to your domain or IP being blocked by firewalls or blacklists.
- Loss of trust: Clients or users who discover a copied site may view your business as unoriginal, unprofessional, or unethical.
- Potential lawsuits: In commercial or high-traffic cases, unauthorized duplication may result in cease-and-desist letters or formal legal action.
When in doubt, stick to white hat practices, use ethical hacking for research only, and always duplicate websites you own, have built, or have permission to work on.
Summary
Creating a duplicate website can help web developers for a variety of reasons, including learning and contribution, backup, testing and development, and so on.
If you are reproducing a website to learn from it or use it as inspiration for your own, making significant changes may not have an impact on you or put you in breach of any copyright laws.
Nonetheless, duplicating a website without permission or for illegal purposes is neither advised nor encouraged.
Authors note
The webpage mentioned in this post was copied for educational purposes and was not meant to be used maliciously or to cause harm. We acknowledge that the example in this article may contain copyright material, and we have made sure to properly credit the primary source.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I afford a website builder?
Yes. Besides paid website builders, there are also free ones; however, they come with fewer options.
Why should I create a website?
There are many reasons why you should create a website if you’re an artist. You can use it to create a place where people can learn about you, talk about your art, or show off your work.
Can you migrate my existing website over?
Yes, and without issue. Regardless of how many websites you’re managing, we’ll bring all of them under the Verpex wing free of charge. Just send us the details of your websites when you’ve signed up to get started.
How is the website maintenance carried out?
On a daily basis, software, hardware, vulnerability, MariaDB, CloudLinux paths and cPanel updates are carried out on our servers without a reboot. However, if we have to carry out any maintenance that includes some downtime, we schedule in advance and update our status page

Jessica Agorye is a developer based in Lagos, Nigeria. A witty creative with a love for life, she is dedicated to sharing insights and inspiring others through her writing. With over 5 years of writing experience, she believes that content is king.
View all posts by Jessica Agorye





















