The term "The Internet of Things (IoT)" is somewhat jovial; at first mention, it is easy to assume it is a book or movie title; what you must know, however, is that this term captures something phenomenal.
The meaning and attributes of the internet of things are truly profound, and it all started with the discovery of the internet. The internet, a nonpareil, was officially introduced publicly in 1983 and has since taken over the world. As of January 2022, 4.95 billion people, an equivalent of 62.5% of the world's population, are on the internet with an average use time of 7 hours daily, making the internet an integral part of our society.
The question then becomes, what is the marvel that is "the internet of things"? How was the name coined? What purpose does it serve, and why are we looking into it?
To start off, let us address why we are looking into the internet of things (IoT). Our research into IoT is to deliver more insights as to its meaning. Every internet user should be aware of how this technology has influenced and will continue to influence our lives, making it easier to understand the purpose it seeks to achieve.
Internet of Things (IoT) Defined
The internet of things (IoT) is a network of interconnected or embedded digitally connected physical objects [smart devices]. These devices have internet connectivity, software, processing ability, sensors, and other technologies provided with unique identifiers (UIDs) that allow communication via connection and data exchange with other devices, systems, and control via the web without requiring human interactions over a wireless network.
Command or information requests can be given over an IoT device using a remote [a smartphone, a tablet, or any device that can serve as a tool for control]. The phrase “the internet of things “ was devised by Kevin Ashton an innovator and consumer sensor expert, who described it as the network that connects physical objects to the internet. The purpose of IoT, like every other technology ever created before, is to make life easier and more accessible, by creating an ecosystem where everything is interconnected.
How Does the Internet of Things Work?
IoT is possible through its ecosystem, consisting of web-enabled smart devices that use embedded systems such as sensors, actuators, processors, and communication hardware. These systems send and act on data they acquire from their environments, shared via the cloud, and integrated with software that proceeds to analyse and transmit the data via an app or website.
The IoT has also evolved and does not need to be connected to the public internet to work; it can be connected to a network and be individually addressable. IoT can be found in an array of devices, industries, and settings; it is majorly synonymous with products pertaining to the concept of the "smart home" and is also largely used in the healthcare system.
Literally, any physical object can be transformed into an IoT device as long as it has an internet connectivity feature, can support one or multiple systems, can be controlled, and can communicate information.
If you have noticed, many IoT devices have the word "SMART" in front, like your smart TV, wristwatches, smart home, smart cars, etc. The technological wave of making obtuse things smarter is on the rise. Other examples are smart toilets, toothbrushes, mirrors, and guess what? Even refrigerators now communicate with your phone, reminding you of what one might consider peripheral like you are about to run out of milk or your groceries are about to expire. It is indeed the internet of everything.
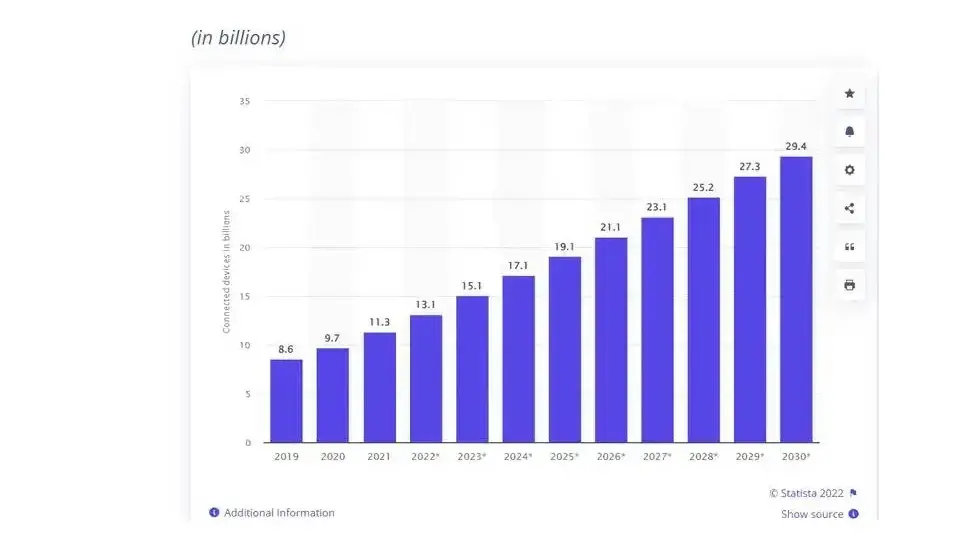
According to IoT analysis, connected devices grew by 8% in 2021, and a report by Statista states that in 2022, there will be 13.1 billion IoT-connected devices, a number projected to increase to 29.4 billion in 2030. In ranking countries by their usage, China came out as the highest consumer and is predicted to lead the world as the highest consumer by 2030. This is because China is very ambitious in creating new technologies.
4 Components of IoT
The internet of things(IoT) has four basic components:
1. Sensors or devices
They collect data from their environment, which could be as simple as reading the pressure in a gas or liquid or taking a temperature reading.
2. Connectivity
The sensors and devices are connected through various network connectivity methods like cellular, satellites, Bluetooth, WiFi, etc.
3. Data processing
This starts from the sensor to the cloud, and the software begins to process data received in real time.
4. User interface
Processed data is presented to the end user, which can be via text, alerts, notifications, etc.
IoT In Different Industries
- Medicine
IoMT (Internet of Medical Things) is specific to healthcare and medical applications. It is the network of interconnected medical devices and software applications for healthcare information technologies.
IoMT enables the use of communication technologies for remote healthcare services. People can transmit medical data from their houses to their physicians; this data collection would aid the physician in knowing the best treatment for the patient.
Physicians can also prescribe medications by checking patients' data without having the patient visit the hospital. Wearable devices can track and monitor health metrics like irregular heartbeats or alert diabetic patients of fluctuations in glucose levels. There are many examples of the impact of IoT in medicine, and the intent is to make healthcare cheaper and more efficient.
- Fintech
The purpose of the IoT is to capture data, process it, and use this data to provide the necessary outcomes. This is beneficial in the banking industry because data happens in real-time, which means data is updated quickly.
IoT payments allow customers to pay bills using cards, faces, smartphones, and watches, promoting a cashless society. There are IoT devices compiled with machine learning to detect irregularities from payment portals and servers, which help to identify risk or fraudulent activities.
- Manufacturing
IoT in manufacturing will enable factories to become smarter to maximise production. Sensors are used to measure sources of data in real time for monitoring production, tracking, and tracing products. There are also devices that can be integrated for automated reporting and auditing.
- Agriculture
The Internet of things enables devices and sensors to collect data that would help farmers monitor their work, climatic conditions, soil, water, and field conditions.
This is possible through smart irrigation, which automates the irrigation process to ascertain both the soil and weather conditions, informing you of the best process or method to follow when planting. There are so many examples of smart agriculture that concern not only plants but animals as well, like livestock health monitoring, etc.
- Education
Thanks to IoT Augmented reality is possible for a better learning experience, giving students a somewhat real-life experience of their lessons.
There are devices like headbands that students put on in classrooms that can monitor their concentration levels. This data is transmitted to the teachers' laptops and then to the parents. In other words, in a classroom full of students, a teacher can tell which child is not paying attention. There are also sensors to track school buses and smart attendance systems to manage the attendance records of students at different levels.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Internet of Things
To fully understand the internet of things, we must ask, is this a digital revolution or evasion? This ecosystem connects everything together, what is the benefit for us in our society, and what are the limitations we experience or will experience by engaging and partaking with this technology?
Advantages of IoT
- The IoT offers assistance in developing more innovative homes and cities, enhancing the quality of life and security. Examples are smart traffic monitoring for traffic flow, smart home security systems for monitoring break-in attempts, e.g. ring an alarm and ADT home security app, etc.
- Updates are in real-time, which means that information is accessible anywhere in the world, whether far or near.
- IoT helps save energy. Examples are smart management, monitoring equipment and preventing overload, smart controls for lighting, and thermostats that automatically set the temperature of an environment based on weather conditions and measure natural light, adjusting the lighting of a room as required.
- IoT saves effort because it requires no human interaction to perform tasks.
Disadvantages of IoT
- Abusers take advantage of this technology to stalk and harass individuals. There have been cases where stalkers hack into their victims' homes, intruding on their privacy to evoke fear of violence.
- Unskilled workers are at a high risk of losing their jobs. Devices have been created to replace different roles, leaving people out of their jobs in exchange for cheaper labour and costs. For example, smart irons have replaced ironmen, smart washing machines have replaced dry cleaners, and according to Oxford Economics on BBC news, robots will replace 20 million manufacturing jobs by 2030.
- Over-reliance on IoT devices makes people use less of their intellectual capacity because they heavily rely on smart devices instead of doing physical or mental work.
Conclusion
The IoT promises to make our environment smarter, more measurable, easier to monitor what's going on inside and outside, provide a better understanding and save us time and energy. The biggest downside at this moment is the security risk. The IoT collects a lot of sensitive and vital data, and many of these devices have been left open to hackers. While the stacks are higher with IoT networks with the potential risk of hijacking, we can admit that IoT bridges the gap between the physical and digital worlds. The possibilities are endless with this system. We have established its connectivity across several industries, but we are only scratching the surface as a lot more can be accomplished.
The imagination of what is possible in the digital world is endless. Back in 1980 at Carnegie Mellon University, the first internet appliance, a coke machine, was tested to ascertain the status of the machine to report its inventory and ascertain if newly loaded drinks were hot or cold. Now, in 2022, there are millions with access to smart devices. We went from M2M, where machines connect with each other without human interactions using a network, to the IoT ecosystem, where devices interact with each other as well as humans, collecting, sending, and acting on the data acquired from their environment. That’s how grand the technology is. In conclusion, technology was created to know everything happening within us and around us. There are so many challenges that come along with IoT. Do the advantages outweigh the disadvantages? What does this really mean for the future of the world?
I guess we’ll just have to wait and see more possibilities unfold.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is hosting free?
There are many different hosting plans on the market, and some of them offer a free hosting option.
Why choose WordPress hosting?
WordPress is so popular because it allows people to create websites with total customization. With hundreds of apps available for one-click installations, creating something that’s eye-catching and unique is much easier with a CMS like WordPress .
What’s the difference between shared hosting and WordPress hosting?
Shared hosting is a catch-all term for shared hosting services. WordPress hosting is a specialized hosting that’s optimized to the WordPress content management system. You can learn more about CMS WordPress on our blog.
What extra functionality comes with dedicated hosting?
Just about everything you can think of. You can host numerous web applications, run a gaming site, implement machine learning tools, apply your own security, and much more.

Jessica Agorye is a witty creative in love with life. She is based in Lagos Nigeria and is currently working on being a full-stack developer. She has worked as a content developer for over 5 years and believes that content is king.
View all posts by Jessica Agorye

















